Hello friends!
Thank you for following series of blog posts on this Study Guide for AZ-305!
This is the final (Part 12/12) of blog post series to help you get ready for the latest AZ-305 exam.
Feel free to check the previous posts listed below, if you did not look into them yet 🙂
Table of content (blog series)
- Part 1: Design a governance solution
- Part 2: Design Authentication and Authorization Solutions
- Part 3: Design a solution to log and monitor Azure resources
- *** Design Infrastructure Solutions ***
- Part 4: Design a compute solution
- Part 5: Design an application architecture solution
- Part 6: Design a network infrastructure solution
- Part 7: Design a migration solution
- *** Design Data Storage Solutions ****
- Part 8: Design a non-relational data storage solution
- Part 9: Design a data storage solution for relational data
- Part 10: Design a data integration solution
- *** Design Business Continuity Solutions ***
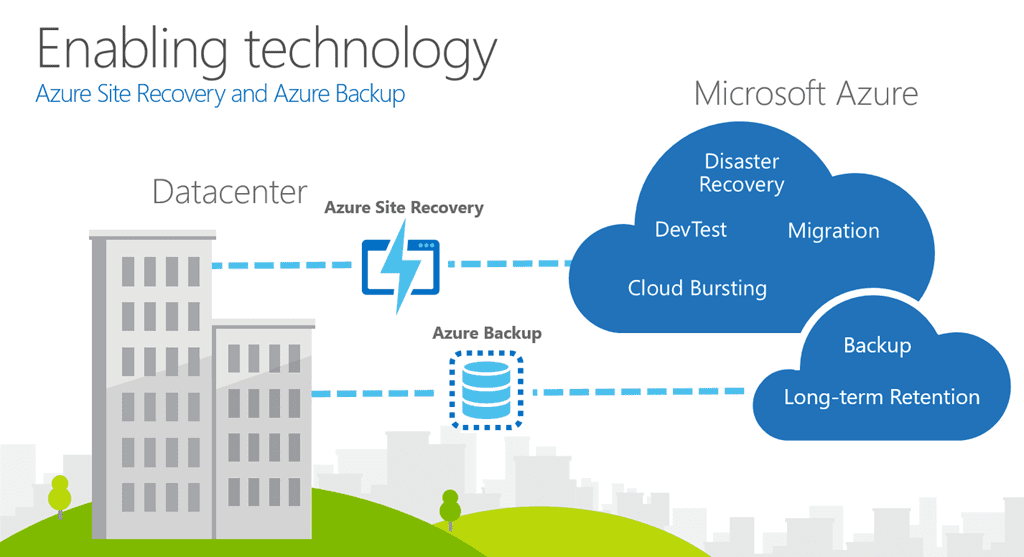
- Part 11: Design a solution for BC, Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Part 12: Design for high availability
What is high availability ?
High availability (HA) is an important quality measure of computing infrastructure that is mission-critical for the customer facing applications and overall organization’s systems. High availability permits the computing infrastructure to continue functioning, even when certain components fail.
Thus, cloud solution providers (CSPs) are expected to deliver certain measures and guarantees to claim the high availability of the offered services.
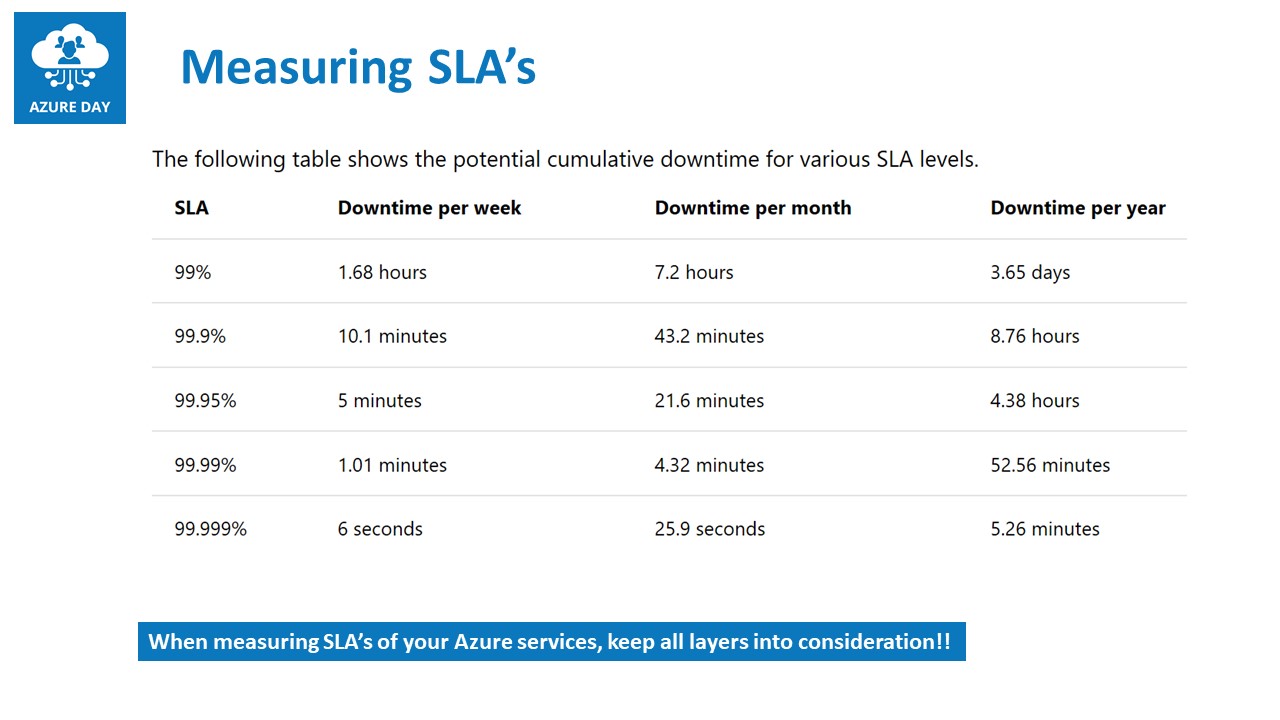
The diagram below, equates Service Level Agreement (SLA) percentual to actual downtime, measured in seconds per week, month and year.
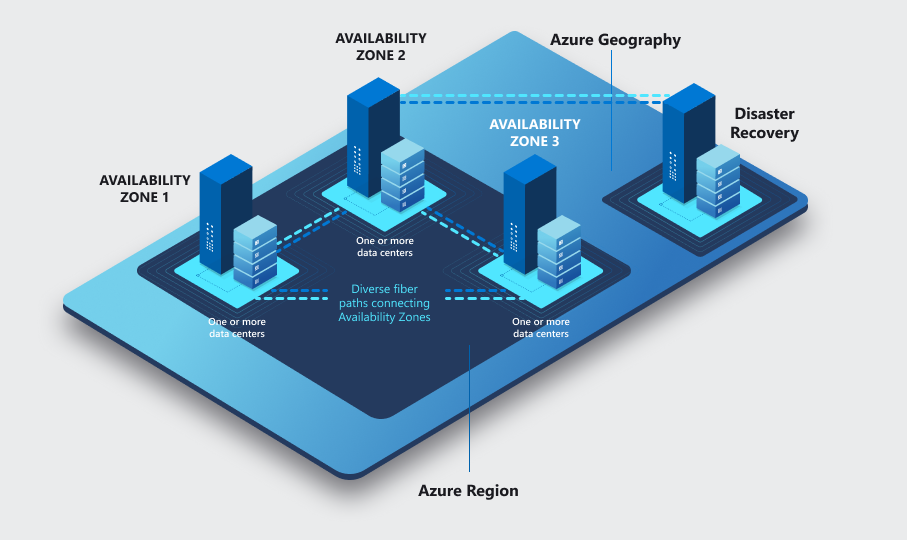
How to achieve High Availability in Azure?
Azure infrastructure is composed of geographies, regions, and availability zones which in turn limits the impact of a physical server or Sofware update failure and therefore limit potential impact to customer applications and data.
The Azure availability zones construct was developed to provide a software and networking solution to protect against datacenter failures and to provide increased high availability (HA) to the Azure customers.
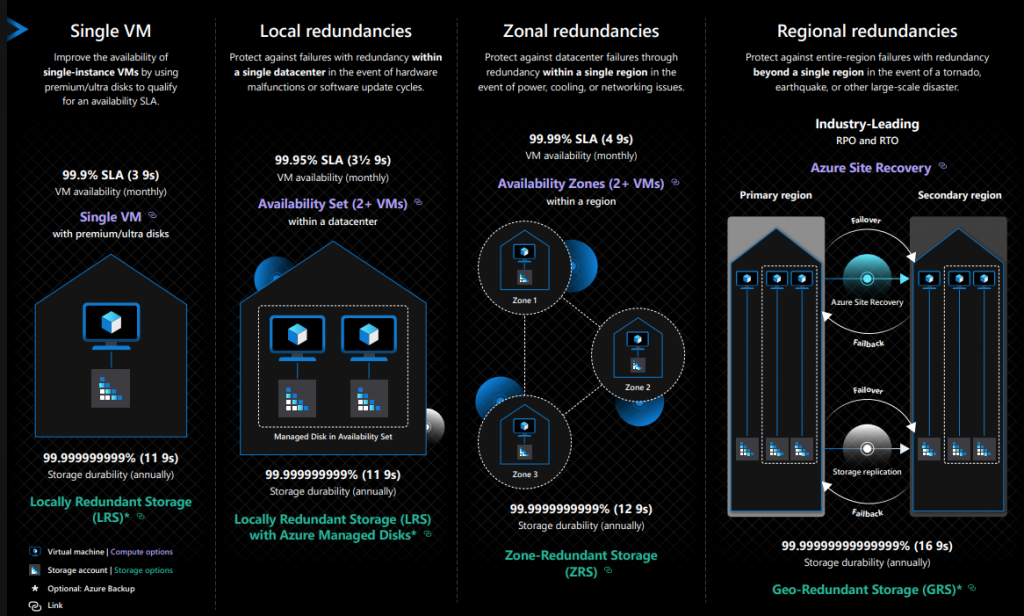
Availability zones are playing very important role in designing your HA solution to meet customer needs. Please, read more about the Azure Regions and availability zones here.
Part 12: Design for high availability
The references below are taken from official Microsoft docs and focused on designing HA solutions in Azure. You could also find it helpful to check the Microsoft docs and learning paths with [Tutorials] below 😉.
This collection of links is gathered with a focus on the exam objectives of the AZ-305 certification exam.
Regions and availability zones
Azure geographies
Azure services that support availability zones
[Article] Enabling Data Residency and Data Protection in Microsoft Azure Regions
Azure reliability Overview
Build solutions for high availability using availability zones
Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework
Reliability Patterns
High availability and disaster recovery scenarios for IaaS apps
Infographic: Reliability with Microsoft Azure
[Tutorial] Design for high availability
[Tutorial] Configure virtual machine availability
[Tutorial] Describe high availability and disaster recovery strategies
[Tutorial] Monitor the usage, performance, and availability of resources with Azure Monitor
[Tutorial] Plan and implement a high availability and disaster recovery environment
[Tutorial] Deploy highly available solutions by using Azure SQL
SUMMARY
This is it folk, we did it!!!
Thank you for visiting the AZ-305 Study Guide and checking the Part 12: Design a solution for backup and disaster recovery and completing your learning journey.
Looking forward and ask for feedback.